#WhiteRustPrevention #AlbugoCandida #FungalDisease #Agriculture #CropProtection
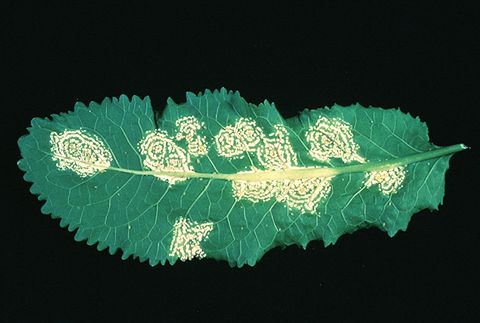
White rust caused by the Albugo candida is a serious fungal disease that affects plants in the Brassicaceae family, including popular crops such as broccoli, cauliflower, and cabbage. This disease is capable of causing significant yield losses, which can result in major economic impacts on farmers and the food industry as a whole. Therefore, it is essential to understand the development of this disease, its symptoms, and the measures that can be taken to prevent its spread.
Albugo candida thrives in moist and humid conditions, making it particularly prevalent in regions with high rainfall or areas with poor air circulation. The fungus can quickly spread through the plant tissues, causing yellow or white blisters on leaves, stems, and other plant parts. These blisters can eventually rupture, releasing spores that can infect other plants in the vicinity. In addition to the direct damage it causes to the plant, the disease can also render crops unmarketable due to its unsightly appearance and reduced nutritional value.
Fortunately, there are several strategies that farmers can use to prevent and control the spread of white rust. These include planting resistant cultivars, crop rotation, and the use of fungicides. Farmers can also adopt cultural practices that promote good air circulation and reduce moisture levels, such as pruning and controlling weeds. By implementing these measures, farmers can reduce the incidence and severity of white rust, improving crop yields and protecting their bottom line.
White rust caused by Albugo candida is a significant threat to the Brassicaceae family, and effective measures must be taken to prevent its spread. By understanding the development of this disease, its symptoms, and the measures that can be taken to prevent its spread, farmers can protect their crops and ensure a healthy food supply for consumers.