#AlternariaBlight #AlternariaBrassicicola #CruciferousCrops #FungalPathogen #GeneticResistance #Fungicides #BiocontrolAgents #CropRotation #SanitationPractices #Sustainability #Agriculture
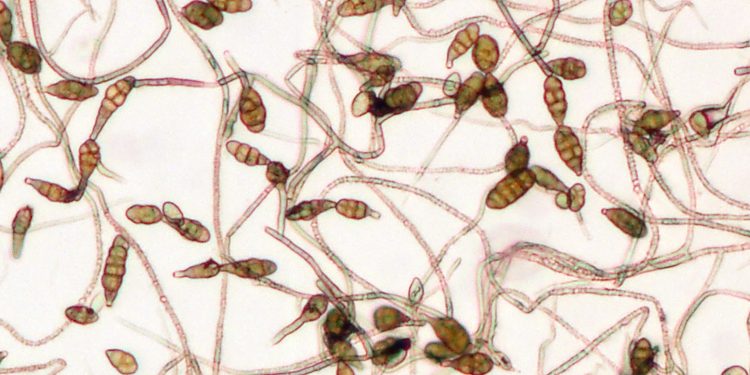
Alternaria blight, caused by the fungal pathogen Alternaria brassicicola, is a major concern for farmers and gardeners alike, as it affects a wide range of crops, including cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower. This disease can cause significant yield losses and reduce the quality of produce, leading to economic losses for growers. In this article, we will delve deeper into the causes and consequences of Alternaria blight and discuss strategies to manage and prevent its spread.
Alternaria brassicicola thrives in warm, humid conditions, and can spread quickly in fields with poor air circulation. The fungus can infect both young and mature leaves, causing brown or black lesions that can expand rapidly and eventually cover the entire leaf. In severe cases, the disease can also affect the stems and flower heads, leading to wilting and premature death of the plant.
To prevent the spread of Alternaria blight, farmers and gardeners should practice good sanitation measures, including removing infected plant debris and using clean seeds and planting material. Crop rotation can also help to reduce the incidence of disease, as can the use of fungicides and biocontrol agents.
In recent years, researchers have also been exploring the use of genetic resistance as a means of managing Alternaria blight. By identifying genes that confer resistance to the pathogen, breeders can develop new cultivars that are less susceptible to the disease. This approach has the potential to reduce the reliance on chemical fungicides and improve the long-term sustainability of agriculture.
Alternaria blight caused by Alternaria brassicicola is a serious threat to cruciferous crops. To manage and prevent the spread of this disease, it is important to adopt good sanitation practices, use fungicides and biocontrol agents, and explore the use of genetic resistance in breeding programs.