#BrownSpotFungus #Pseudocercosporellacapsellae #Agriculture #FungalDisease #CropManagement #PlantPathology #Fungicides #PlantResistance
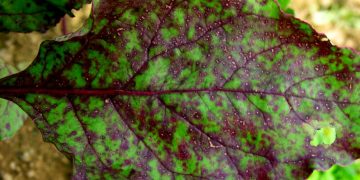
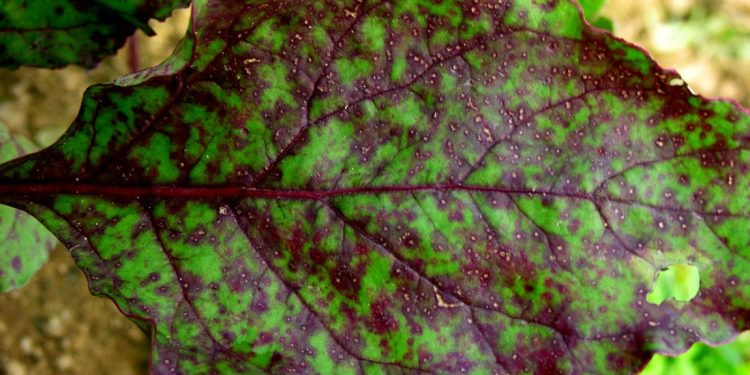
Pseudocercosporella capsellae, commonly known as Brown Spot Fungus, is a plant pathogenic fungus that affects several crops, including canola, mustard, and other cruciferous vegetables. This fungal disease is a significant concern for farmers and agricultural industries worldwide, as it causes significant yield losses, reduces the quality of the produce, and lowers market value.
The development of Brown Spot Fungus starts with the appearance of small brown spots on the leaves, which then spreads to other parts of the plant, including pods, stems, and seeds. The fungus can survive in the soil and plant debris, making it difficult to eradicate from the affected area. The spores of Pseudocercosporella capsellae can also spread through the wind or water, causing the disease to spread to other crops and fields.
The consequences of Brown Spot Fungus can be devastating for farmers, leading to significant economic losses and food shortages. The disease can also affect the quality of the produce, making it unsuitable for consumption or processing. Therefore, it is essential to understand the causes and symptoms of this fungal disease to implement effective preventive measures and treatment options.
One of the best ways to control Brown Spot Fungus is through the use of resistant plant varieties, crop rotation, and proper soil management. Farmers can also use fungicides to prevent and treat the disease, but this method can be costly and may have adverse environmental impacts. Therefore, it is crucial to use fungicides responsibly and only as a last resort.
Brown Spot Fungus, caused by Pseudocercosporella capsellae, is a severe threat to agriculture, leading to significant yield losses, reduced quality of the produce, and lower market value. Farmers and agricultural industries must take preventive measures and implement appropriate treatment options to control the spread of this fungal disease and minimize its impact on crops and food production.