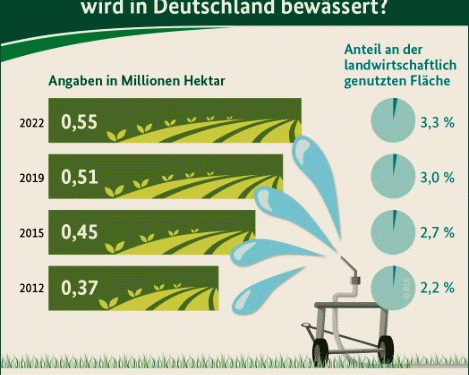
The agricultural landscape in Germany is experiencing a significant transformation, with a notable increase in the use of irrigation systems over the past decade. According to recent data, the irrigated agricultural area in Germany expanded from 0.37 million hectares in 2012 to 0.55 million hectares in 2022, marking an almost 50% growth. Despite this increase, Germany’s agricultural water demand remains relatively low on a global scale, with only 3.3% of its agricultural land being irrigated in 2022.
This rising trend in irrigation is particularly pronounced in the cultivation of vegetables, strawberries, and potatoes. Nearly 60% of the open-field area dedicated to vegetables and strawberries, and 44% of the potato cultivation area, relied on irrigation in 2022. This significant reliance underscores the importance of water management in ensuring the productivity and quality of these crops.
Germany’s approach to irrigation reflects a broader trend of adapting to changing climatic conditions and the increasing frequency of droughts. The summer months, in particular, have seen reduced rainfall, making irrigation essential for maintaining crop yields. Farmers and agricultural engineers are increasingly turning to advanced irrigation technologies and water management practices to optimize water use efficiency and support sustainable agriculture.
While the overall percentage of irrigated land in Germany is relatively low compared to countries with more arid climates, the strategic use of irrigation in high-value crops like vegetables, strawberries, and potatoes highlights its critical role in the agricultural sector. These crops are particularly sensitive to water stress, and effective irrigation can significantly enhance their growth, quality, and market value.
Innovations in irrigation technology are also playing a crucial role in this transformation. Precision irrigation systems, which include drip and sprinkler systems, are being adopted to ensure that water is applied directly to the root zones of plants, minimizing water wastage and maximizing efficiency. Additionally, soil moisture sensors and automated irrigation systems are being employed to optimize irrigation schedules based on real-time data, further enhancing water use efficiency.
The German Federal Office for Agriculture and Food (BLE) has been instrumental in promoting efficient irrigation practices and supporting research initiatives aimed at developing sustainable water management strategies. These efforts are essential in addressing the challenges posed by climate change and ensuring the resilience of Germany’s agricultural sector.
The substantial increase in irrigated agricultural land in Germany over the past decade underscores the growing importance of water management in the face of changing climatic conditions. While the overall water demand in Germany’s agriculture remains low globally, the strategic use of irrigation for high-value crops like vegetables, strawberries, and potatoes is crucial for maintaining productivity and quality. Continued innovation and adoption of advanced irrigation technologies will be key to ensuring sustainable water use and the resilience of Germany’s agricultural sector.